Identity Verification definition
Identity Verification has evolved significantly from traditional paper-based methods such as passports and national ID cards to modern digital techniques like contactless palm recognition and facial recognition. Today, it includes technologies like electronic IDs and AI-driven verification to ensure a user is who they claim to be.
What is Identity Verification?
Identity verification is the process of confirming an individual’s identity by comparing their identifying information or documents (such as an ID card, biometrics, or personal data) against reliable sources. This ensures the person is who they claim to be before granting access or services. An ID verification service can check these documents thoroughly, to a very high level of accuracy, often remotely via online identity verification.
There are several different ways to carry out identity verification:
- The process works by comparing a person’s unique characteristics (e.g., facial biometrics or fingerprints) with verified data held by an officially recognized source, such as a passport or national ID card.
- It also includes checking the accuracy of submitted identity details and analyzing supporting documents to detect potential fraud or human error.
- Verification systems often assess the authenticity of government-issued documents using advanced technologies.
- This can be done in real-time to quickly return results and avoid delays in verification.
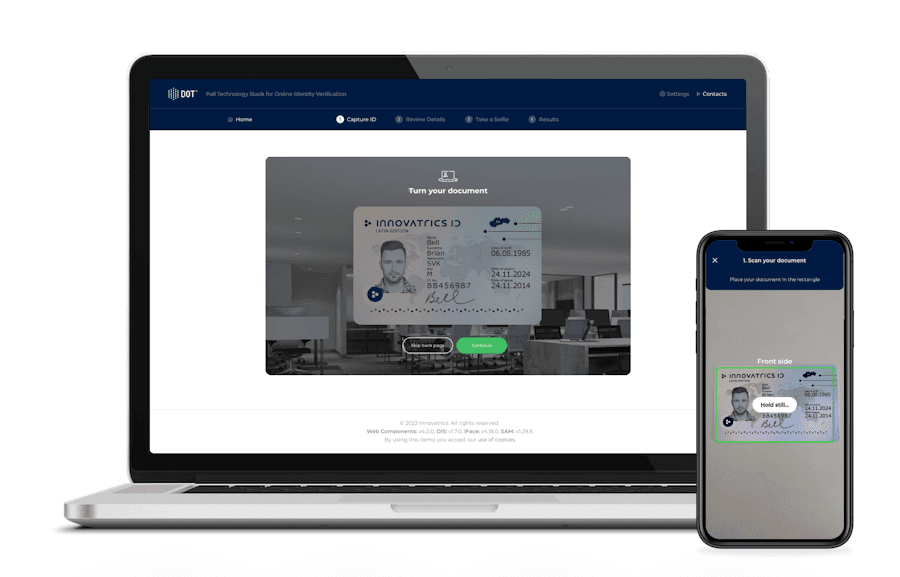

Identity Verification vs. Identity Authentication
It’s important to distinguish identity verification from identity authentication, as the two terms are related but not identical:
- Identity verification is the process of confirming that someone is who they claim to be. This is often done during onboarding or enrollment. It involves collecting and verifying identifying documents, such as a passport or driver’s license, and comparing them against trusted data sources. For example, this process can involve comparing details on a government-issued ID with a selfie and verifying the ID’s authenticity.
- Identity authentication, on the other hand, is the process of confirming that a previously verified user is indeed the same person trying to access a system or service. For instance, when a user logs into a secure system, entering a password or providing a fingerprint is a form of identity authentication (verifying they are the authorized user). While initial identity verification establishes who a user is, authentication is the ongoing process of proving that verified identity, typically through credentials or biometrics.
By clarifying these terms, businesses and organizations ensure they apply the right processes.
Both identification and authentication are critical components of a robust security framework.
However, they serve distinct purposes and occur at different points in a user’s interaction with a system or service.
What is Online (Remote) Identity Verification?
Online or remote identity verification is a pretty straightforward process. Instead of physically taking a photo ID and other forms of written information for someone to manually check, the process takes place over the internet. The user captures a photo of themselves and uploads it to the identity verification platform. Here, it is checked against a list of document-related trust factors, including document expiration, valid MRZ checksum, text consistency, black and white photocopy detection, and screen attack detection. In addition, biometric-related trust factors such as face match, passive/active liveness, age, and gender consistency are analyzed.
The online process also enables the uploading of scanned or photographed documents for analysis. Identity verification can take place then and there, or it may take time for everything to be checked and verified. Either way, it reduces time spent travelling to have physical copies verified and minimizes the cost and inconvenience of producing multiple certified copies of important documentation.
Identity Verification Methods
Identity verification methods differ based on the type of ID presented, the purpose of verification (such as onboarding, access control, or regulatory compliance), and the level of security required.
Modern solutions typically combine biometric technologies, document verification, and data checks to accurately and securely confirm an individual’s identity.
Document Verification
Document verification involves confirming the authenticity, accuracy, and suitability of documents for their intended purpose. This process is crucial for identity documents like driver’s licenses, ID cards, and passports to ensure they genuinely represent the individual.


Facial Recognition
Facial recognition matches a live image (selfie or video) against the photo on an official ID to verify that the user is the legitimate owner. Advanced facial recognition systems also detect signs of presentation attacks, such as the use of printed photos, masks, or screen replays, to prevent spoofing attempts. In certain scenarios, facial data is checked against internal or governmental databases to uncover potential identity theft or multiple accounts associated with one person.


Liveness Detection
Liveness detection uses algorithms to determine if a biometric sample is from a real, living person, not a fake. When users submit facial photos, these algorithms can tell the difference between a live individual and presentation attacks like masks, photos, or videos.


Benefits of Identity Verification
Identity verification methods offer many benefits. These include enhancing security and preventing fraud to streamlining user onboarding and building trust. By confirming that individuals are who they claim to be, businesses and institutions can protect sensitive data, comply with regulations, and create safer, more reliable digital experiences.
Fraud Prevention and Security
Advanced identity verification stops fake or stolen identities from being used to open accounts or access systems. This capability is vital in mitigating identity theft, financial fraud, and related abuses.
Regulatory Compliance
Verifying customer identities is a strict regulatory requirement (Know Your Customer, Anti-Money Laundering, etc.) across many industries. Effective identity verification helps businesses comply with laws and avoid penalties. It also strengthens security by confirming legitimate users, deterring crimes like money laundering and terrorist financing.
Building User Trust
Knowing that a service verifies identities can boost end-user trust. People feel more secure on platforms prioritizing security. For businesses, IDV protects their reputation by mitigating fraud and unauthorized access. This trust is crucial for fintech apps, online marketplaces, telcos, and any platform dealing with sensitive data.
Seamless Access with Minimal Effort
Modern identity verification can streamline onboarding. Instead of requiring in-person verification (which is slow and inconvenient), digital IDV allows users to quickly verify their identity from a smartphone. This reduces drop-off in customer onboarding flows. A quick selfie and ID scan is faster than visiting a branch, thus improving conversion rates for businesses while still ensuring security.
Access to Services and Opportunities
Reliable identity verification for individuals fosters inclusivity and convenience by enabling remote access to essential services like banking, government services, and age-restricted products. This capability is particularly significant in online education, e-voting and healthcare, providing secure access without the need for physical presence. In the digital economy, proving one’s identity online unlocks instant access to crucial services.
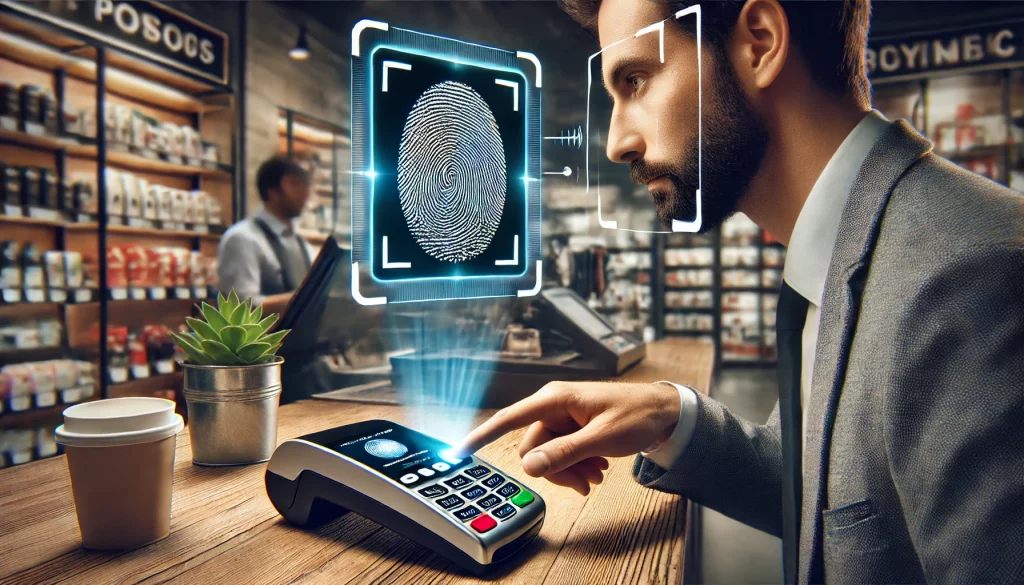
The Role of Biometrics in Identity Verification
Biometrics focuses on a person’s unique characteristics, such as fingerprints, iris and retina scans, facial features, and palmprints. These are unique to each person, making them a highly effective identity verification tool. Advantages include the fact that they are extremely difficult to fake or manipulate. The person will not lose, damage, or forget to bring them along to an identity verification session. Moreover, they are quick and easy to process.
Many online and in-person ID verification methods involve the use of biometrics. Fingerprint scanning pads, retina or iris scanners, palm readers, and facial recognition software can all produce highly accurate results in a very short space of time. Biometrics can also help authenticate photographs and selfies provided by the person for remote ID verification. The process is also highly effective when it comes to analyzing biometric ID documents and passports.
Why Identity Verification Is Needed
While identity verification may seem like a given to industry professionals, clearly outlining its importance helps connect the technology to the real-world problems it solves.
Rising Identity Fraud and Theft
Identity fraud is at an all-time high. With so much of life and business moving online, criminals have more opportunities to impersonate others or create fake identities. In 2023, the FBI reported that identity-related crimes resulted in $8.8 billion in losses. Without identity verification measures in place, anyone could claim to be someone else to exploit systems, leading to financial loss, data breaches, and damaged trust.
Account Takeovers and Cybersecurity
Even after initial onboarding, verifying identity is crucial to prevent account takeovers. Multi-factor authentication (a form of verifying identity at login) is a response to the wave of stolen passwords and session hijacks. Essentially, identity verification ensures that the person accessing an account or service is the legitimate account owner. Without it, even strong passwords can be bypassed via phishing or credential stuffing attacks.
Regulatory Requirements
Many sectors legally require verifying customer identity. Banks, financial institutions, cryptocurrency exchanges, and gambling sites are mandated by KYC and AML laws to verify identities. These regulations exist because identity verification is a first line of defense against money laundering, fraud, and even terrorism financing. Compliance is a non-negotiable reason why organizations implement identity verification. Failing to do so can result in heavy fines or shutdowns. For instance, regulators might require verifying a customer’s identity before allowing any transactions or withdrawals to ensure traceability of funds to a real person.
Protecting Customers and Business Reputation
Customers expect their personal information and assets to be safe. If an impostor can easily bypass security due to a lack of proper ID verification, customers lose confidence. High-profile breaches or fraud cases can severely damage a company’s reputation. Thus, companies need identity verification not only to protect themselves but also to protect their users from identity theft. This is particularly relevant for services dealing with sensitive data, such as healthcare portals, insurance, education records, etc.
Enabling Digital Transformation
Finally, identity verification is a key enabler for digital transformation. As services move online, from opening bank accounts to signing legal documents digitally, having a reliable way to verify “you are who you say you are” remotely is fundamental. Without it, organizations would have to rely on in-person verification, which doesn’t work at scale. In other words, businesses need secure digital identity verification to unlock the convenience and efficiency of online services in a trustworthy way.


Real-World Applications of Identity Verification
The practical application of identity verification spans various sectors. Outlining use cases helps illustrate how and where these processes are applied in the real world.
Identity Verification in Financial Services and Banking
Banks, fintech startups, and crypto platforms use identity verification when onboarding new customers. For example, when you open an online bank or trading account, you’ll be asked to submit a photo of your ID and perhaps a selfie. This ensures the bank knows its customer (KYC) and reduces the chance of fraud or fake accounts.
Public Sector Services and e-Government
Applying for government aid, social services, or digital IDs (like national digital identity programs) often requires verification. Governments need to ensure that benefits or services are granted to the right individuals. Identity verification is employed in various contexts, such as confirming eligibility for unemployment benefits or access to tax portals. In some countries, identity verification is used for e-voting or issuing travel eVisas, where citizens verify their identity online to participate.
Travel and Border Control
An increasingly digital example is applying for a visa or electronic travel authorization. Applicants scan passports and may go through a facial verification step. Airlines and border agencies also explore remote ID verification to speed up check-in or immigration.
Remote Employee and Contractor Onboarding
Companies use identity verification for hiring and onboarding employees or contractors, especially in remote work scenarios. Verifying the identity of a new hire remotely is a use case often called workforce identity verification. This ensures the person hired is who they claim to be, preventing credential fraud or misrepresentation in hiring.
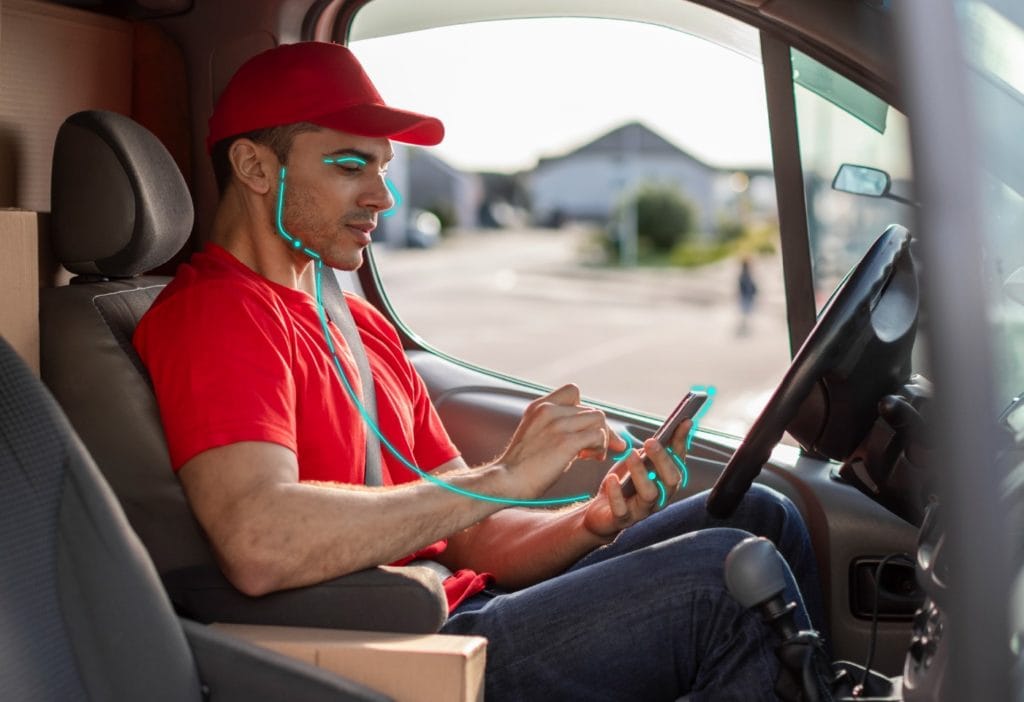
Ride-Sharing and Transportation
By verifying the identities of users through government-issued IDs, facial recognition, or biometric checks, platforms like Uber and Lyft can prevent account misuse, impersonation, and fraud. This process not only helps confirm that the person behind the wheel matches the registered driver profile, but also reassures passengers that they are entering a secure and verified environment, boosting overall confidence in the service.


Age-Restricted Content or Purchases
Identity verification is also a solution for confirming age or eligibility. For online sales of alcohol, vaping products, or even online gaming platforms, users may need to verify their identity to prove they are above the legal age. This typically involves an ID check and can include biometric age estimation.
The Future of Identity Verification
The field of identity verification is rapidly evolving. To keep this resource current and authoritative, discussing upcoming trends is crucial:
- Combating Deepfakes and AI-driven Fraud: One of the biggest challenges on the horizon is the rise of AI-generated fake identities (deepfakes for faces, voices, synthetic profile data). The future of IDV will heavily focus on liveness detection 2.0 and deepfake detection. There will be more advanced algorithms to ensure the person on the other end is real and present.
- Continuous Identity Verification: Verifying identities may evolve into continuous models. This could mean periodic reverification or passive monitoring for identity assurance. For example, behavioral biometrics like typing patterns or device usage habits might continuously ensure the same user is operating an account. The concept of “zero trust” in cybersecurity is never trust, always verify. Continuous identity verification extends beyond initial onboarding. Users might be silently verified in the background during sessions, particularly for high-risk transactions.
- Regulatory Evolution and Global Standards: The future of identity verification will be strongly influenced by new regulations. Global standards like ISO/IEC 30107 (which ensures biometric systems can detect if someone is trying to trick them) and NIST guidelines will help define what a trusted and secure system looks like. As regulations and standards become stricter, following them will be essential for any future identity verification solution.
- AI and Machine Learning Enhancements: AI is already playing a dual role. On one hand, it enables fraud (as mentioned with deepfakes). On the other hand, it is integral to advanced IDV. Machine learning models are getting better at document recognition, face matching under challenging conditions, and detecting anomalies. We will likely see AI that can verify an identity document’s security features (holograms, microprint) with expert-level accuracy in milliseconds.
This technology will continue to evolve in response to new challenges, advancements, and changing user expectations. With the rise of AI, identity verification processes and solutions will be crucial for preventing fraud, addressing growing privacy concerns, and meeting increasing regulatory standards.
The future of the industry will rely on continuous innovation, compliance with global standards, and the ability to integrate with trusted digital ID ecosystems. As more services move online, having reliable and secure identity verification will continue to be key to building trust in both government and business sectors.